Physical Changes In The First Trimester
First Trimester of Pregnancy brings along a host of physical changes in a woman’s body. The initial three months of pregnancy are a time of rapid transformation as the body adjusts to the presence of a growing fetus. One of the most noticeable changes is the appearance of the baby bump as the uterus expands to accommodate the developing baby. This expansion can put pressure on the bladder, leading to increased frequency of urination.
Another common physical change during the first trimester is breast tenderness and enlargement. The body starts preparing for breastfeeding, and as a result, the breasts become more sensitive and may increase in size. Additionally, many women experience fatigue and morning sickness, which are also physical symptoms of the early stages of pregnancy.
Furthermore, hormonal changes can lead to skin changes, such as acne or darkening of the skin in certain areas. These changes are completely normal and are part of the body’s response to the pregnancy hormones.
As the body goes through these physical changes, it is important for expectant mothers to embrace these transformations and prioritize self-care to support their overall well-being during the first trimester.
Emotional Rollercoaster: Mood Swings And Hormonal Changes
The first trimester of pregnancy can be an emotional rollercoaster for many women. The surge of hormones, including estrogen and progesterone, can lead to mood swings that can range from feeling elated one moment to being tearful the next. These emotional changes are completely normal and are a result of your body adjusting to the new pregnancy.
It’s important to communicate with your partner and loved ones about these mood swings, so they can understand what you’re going through and offer their support. Seeking comfort from those close to you can help alleviate some of the emotional stress during this time.
It’s also crucial to remember that hormonal changes and mood swings are temporary and typically improve as the pregnancy progresses. Finding healthy ways to cope, such as practicing relaxation techniques or engaging in light exercise, can help manage these emotional fluctuations.
If you find that your mood swings are significantly impacting your daily life, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider. They can provide guidance and support to ensure you are effectively managing your emotional well-being during the first trimester of pregnancy.
Nutritional Needs And Dietary Restrictions
During the First Trimester of Pregnancy, it is important to pay close attention to your nutritional needs and any dietary restrictions that may apply to you. Your body is working hard to support the growth and development of your baby, so it is essential to provide the right balance of nutrients to support a healthy pregnancy.
One of the most crucial nutrients to focus on during the First Trimester of Pregnancy is folic acid. This B vitamin is essential for the early development of the baby’s neural tube and can reduce the risk of certain birth defects. It can be found in leafy green vegetables, citrus fruits, beans, and fortified cereals. It is generally recommended that pregnant women take a prenatal vitamin to ensure they are getting enough folic acid and other essential nutrients.
Additionally, it is important to be mindful of any dietary restrictions that may apply to you during pregnancy. Certain foods, such as unpasteurized dairy products, raw or undercooked meats, and certain types of fish, should be avoided due to the risk of foodborne illness or contamination. It is also important to limit caffeine intake and avoid alcohol entirely during pregnancy to reduce the risk of negative effects on the baby’s development.
Overall, paying close attention to your nutritional needs and dietary restrictions during the First Trimester of Pregnancy is crucial for supporting a healthy pregnancy and the optimal development of your baby.
Managing Morning Sickness And Fatigue
Managing Morning Sickness and Fatigue during the First Trimester of Pregnancy can be challenging for many women. The hormonal changes in the body can lead to nausea and vomiting, making it difficult to keep food down. Additionally, the increased levels of progesterone can cause extreme fatigue, making it hard to stay awake and energized throughout the day. It’s important to find ways to manage these symptoms in order to maintain a healthy pregnancy and overall well-being.
One way to manage morning sickness is to eat small, frequent meals throughout the day. This can help prevent the feeling of nausea that comes with an empty stomach. It’s also important to stay hydrated and drink plenty of water, as dehydration can worsen symptoms. Some women find relief from morning sickness by eating bland, easy-to-digest foods such as crackers, toast, or rice. It’s also helpful to avoid strong smells and spicy or greasy foods, as these can exacerbate nausea.
When it comes to combating fatigue, it’s important to listen to your body and get plenty of rest. Taking short naps throughout the day can help boost energy levels, and it’s also important to prioritize sleep at night. Gentle exercise such as walking or prenatal yoga can also help combat fatigue and improve overall energy levels. It’s crucial to communicate with your healthcare provider about the severity of your morning sickness and fatigue, as they may be able to offer additional tips and recommendations for managing these symptoms.
In conclusion, managing morning sickness and fatigue during the First Trimester of Pregnancy requires a combination of lifestyle changes and open communication with your healthcare provider. By making small adjustments to your diet and daily routine, it is possible to find relief from these challenging symptoms and improve your overall well-being during this important stage of pregnancy.
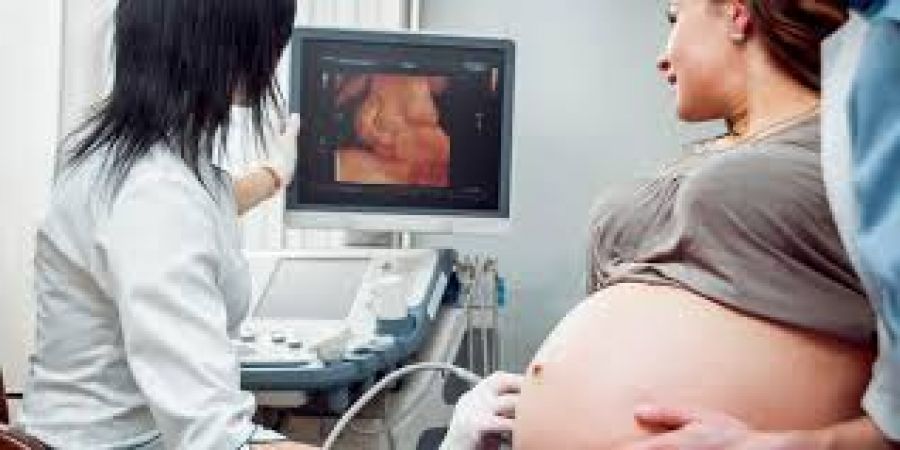
Importance Of Prenatal Care And Medical Check-Ups
During the First Trimester of Pregnancy, it is crucial for expectant mothers to prioritize their prenatal care and medical check-ups. These appointments are essential for monitoring the health and development of both the mother and the growing fetus. Regular visits to healthcare providers allow for the early detection and timely management of any potential complications or health concerns that may arise during pregnancy.
Attending prenatal care appointments also provides expectant mothers with the opportunity to receive valuable guidance and support from healthcare professionals. They can offer advice on nutrition, exercise, and overall wellness, as well as address any questions or concerns that the mother-to-be may have. This personalized care and attention can help expectant mothers feel more confident and informed as they navigate the journey of pregnancy and impending motherhood.
Additionally, prenatal care and medical check-ups are instrumental in ensuring the proper monitoring of fetal growth and development. Through various screenings, ultrasounds, and diagnostic tests, healthcare providers can assess the health and well-being of the unborn baby, identifying any potential issues that may require intervention or specialized care. Early detection and intervention can significantly impact the outcomes for both the mother and the baby, making these regular check-ups an integral aspect of prenatal care.
Overall, the importance of prenatal care and medical check-ups during the First Trimester of Pregnancy cannot be overstated. It is a time for expectant mothers to prioritize their health and well-being, as well as that of their developing baby. By staying proactive and committed to attending these appointments, expectant mothers can take proactive steps to ensure a healthy and successful pregnancy, setting the stage for a positive birth experience and the arrival of a healthy newborn.
Preparing For The Arrival: Setting Up The Nursery And Baby Essentials
As you enter into the excitement of the first trimester of pregnancy, it’s important to start thinking about preparing for the arrival of your little one. One major task to tackle during this time is setting up the nursery and gathering all the baby essentials you’ll need. This is an opportunity to let your creativity shine as you design a space that will welcome your new arrival.
Creating a nursery can be a fun and enjoyable project to take on during your first trimester of pregnancy. From choosing a color scheme to selecting furniture and decorations, there are many decisions to make. Consider the layout of the room and how to best optimize the space for both functionality and aesthetics.
When preparing for the arrival of your baby, it’s crucial to gather all the baby essentials you’ll need. This includes items such as diapers, clothing, bottles, a crib, and a stroller. Making a list of these essentials and slowly checking items off as you gather them can help you feel organized and prepared for your baby’s arrival.
Setting up the nursery and gathering baby essentials can be a meaningful way to bond with your partner and prepare for the new chapter of your lives. It’s a time to come together and envision the future as you eagerly anticipate the arrival of your little one.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the common symptoms during the first trimester of pregnancy?
Common symptoms during the first trimester of pregnancy include morning sickness, fatigue, breast tenderness, and frequent urination.
2. Is it normal to experience nausea and vomiting during the first trimester?
Yes, it is normal to experience nausea and vomiting, commonly known as morning sickness, during the first trimester of pregnancy.
3. How much weight should a woman gain during the first trimester?
On average, most women are recommended to gain 1-5 pounds during the first trimester of pregnancy.
4. Are there any foods or activities to avoid during the first trimester?
During the first trimester, it is generally recommended to avoid certain foods such as unpasteurized dairy, raw fish, and certain types of deli meat. It is also advised to avoid activities with a high risk of falling or injury.
5. What prenatal vitamins are recommended during the first trimester?
During the first trimester, prenatal vitamins that include folic acid, iron, and calcium are commonly recommended to support the baby’s development and the mother’s health.
6. Can exercise be beneficial during the first trimester of pregnancy?
Yes, low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, and prenatal yoga can be beneficial during the first trimester, but it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new exercise routine.
7. How can one alleviate the discomforts experienced during the first trimester?
To alleviate discomforts during the first trimester, it can be helpful to eat small, frequent meals, stay hydrated, get plenty of rest, and manage stress through relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation.